In the following, we will discuss which European countries offer the best conditions for infertility treatment. For this purpose, selected countries in Europe are compared first in terms of costs and then in terms of regulatory conditions for typical infertility treatments, before arriving at an overall assessment in the conclusion.
At the outset, it should be mentioned that the individual success and thus the quality of the fertility treatment should always be in the foreground when choosing a country and a specific clinic for treatment. However, given the good medical care in most European countries, we are convinced that fertility clinics can be found in any country that can ensure a similar level of treatment quality as is the case in Switzerland.
1. cost of infertility treatment

When choosing a place to undergo IVF / ICSI treatment, in addition to the quality of the doctors, the costs also play an important role for many people – especially if, as in Switzerland, health insurance companies do not cover the costs of the treatment (except for clarifying the causes of the unfulfilled desire to have a child).
In the following, we try to make as good a comparison as possible of the costs to be expected for infertility treatment between different European countries. However, a few important notes are in order beforehand that may make comparison difficult and patients should keep in mind when considering the treatment costs listed here.
A few important notes in advance
In the case of infertility treatment, a precise upfront cost estimate and thus an accurate comparison of different offers is difficult for five reasons.
A. Each case is different
Generally, it is difficult to orientate yourself on publicly available price lists or package prices. Treatment costs are always based on the individual case and should always be inquired directly with fertility clinics before making a final decision. It is also possible that after the start of the treatment, due to unforeseen events (e.g. overstimulation of the woman’s ovaries), additional costs may arise (e.g. due to the need to freeze the retrieved eggs).
B. Most of the time it does not work on the first try
Women with an unfulfilled desire to have children should note that in most cases one IVF / ICSI cycle is not enough to get pregnant and bring a healthy child into the world. According to data from Germany, only about 34% of women become pregnant during the 1st cycle. From a medical point of view, researchers consider 6 cycles to be a reasonable upper limit before stopping the attempt to bring a child into the world with IVF / ICSI.
However, the cost of an IVF / ICSI cycle should not simply be multiplied by the number of attempts, often there is a reduction in cost for repeated attempts, but this should be ascertained individually from the clinic treating the patient.
C. Patients need different types of treatment cycles
Basically, three different types of cycles can be distinguished, each with different costs:
- IVF cycle: Here, a cycle extends from the stimulation of egg production to the fertilization of the eggs to the transfer of the fertilized egg
- ICSI cycle: Similar to the IVF cycle, but a more complex method of fertilization of the eggs is performed in the laboratory, which results in higher costs.
- Cryocycle: This is a follow-up cycle after a previous IVF/ICSI cycle. This uses existing frozen eggs and embryos, eliminating the need for costly stimulation but adding thawing costs. Overall, a cryocycle is usually more favorable than an IVF or ICSI treatment cycle
In the following, we focus mainly on IVF and ICSI cycles, however, when inquiring with clinics, patients should also inquire about the follow-up costs of a potentially attached cryocycle.
D. The cost of hormone treatment is often not included in the initial cost estimate and is difficult to accurately estimate in advance
The various medications needed for infertility treatment are rarely included in the initial cost estimate of IVF / ICSI treatment. One of the reasons for this is that medications are usually dispensed by pharmacies rather than by the clinics themselves.
In addition, each stage of the IVF / ICSI treatment process involves different medications and due to unforeseen reactions of the body, it may be necessary to adjust dosages during the course of treatment.
E. Other additional cost blocks besides the “standard package” can lead to surprises
Since fertility treatment is always adapted as specifically as possible to the individual causes of the unfulfilled desire to have a child, other treatment components are sometimes necessary in addition to different hormones for stimulation. Depending on the country and clinic, these may or may not already be included in the “standard package” and will then be invoiced additionally.
Here is a brief overview of typical cost pools in addition to medication costs, some of which are billed separately and some of which are included in the “standard package.”
- Initial consultation
- Laboratory costs (fertilization and cultivation of oocytes and embryos)
- Sperm cell freezing and storage costs
- Freezing of oocytes / embryos (cryopreservation) and storage costs
Switzerland
Switzerland is one of the most expensive countries in Europe to perform fertility treatment.
1st IVF cycle:
Per IVF treatment cycle, patients in Switzerland have to expect costs totaling between CHF 4,000 and CHF 9,000, depending on the effort involved. This includes the cost of the hormone treatment to mature the eggs – depending on the product and the amount of hormone required, this amounts to CHF 1,000 to CHF 2,000. Additional costs may be incurred for
- the freezing and storage of not directly transferred oocytes / embryos of CHF ~700
- annual storage costs of frozen oocytes / embryos from CHF 200 to CHF 1’000
2nd ICSI cycle
For an ICSI treatment cycle, patients in Switzerland must expect total costs of CHF 6,000 to CHF 10,000 , with costs for hormone treatment, freezing and thawing, and annual storage costs of frozen oocytes / embryos corresponding to the IVF treatment cycle. Laboratory costs higher than IVF treatment cycle due to more complex methods.
3rd cryocycle:
For a cryocycle in Switzerland, total costs of about CHF 1,000 to CHF 2,500 per cycle must be expected. In addition, there are the costs of cryopreservation, which can range from CHF 200 to CHF 1,000 per year .
Germany and Austria
Germany and Austria are significantly more favorable than Switzerland across all treatment cycles. The following table provides an overview of typical costs for the three different treatment cycles in Germany and Austria:
| Cycle | Subcategory | Germany | Austria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st IVF cycle |
Total (of which hormones) Additional freezing/storage if necessary |
EUR3’700-5’100 (EUR 700-1’600) EUR 200-500 |
EUR 3’700-5’500 (EUR 400-1’300) EUR ~350 |
| 2nd ICSI cycle | Total | EUR 5’600-7’300 | EUR 4’100-6’000 |
| 3rd cryocycle |
Total Additional storage per year |
EUR800-1’000 EUR 300-600 |
EUR ~1’150 EUR ~380 |
For IVF cycles, the costs in Germany and Austria are similar, for ICSI cycles Austria is slightly cheaper than Germany and for cryocycles the treatment costs are again similar in both countries.
Other European Countries
However, there are a number of other countries in Europe that offer fertility treatments at a high level of quality and at relatively even lower costs than in Germany and Austria (and of course Switzerland).
The following table provides an overview of the costs for IVF / ICSI cycles in Switzerland, Germany and Austria, as well as in several currently popular destinations in Europe for infertility treatments, with the two most favorable countries for the respective treatment method highlighted in each case:
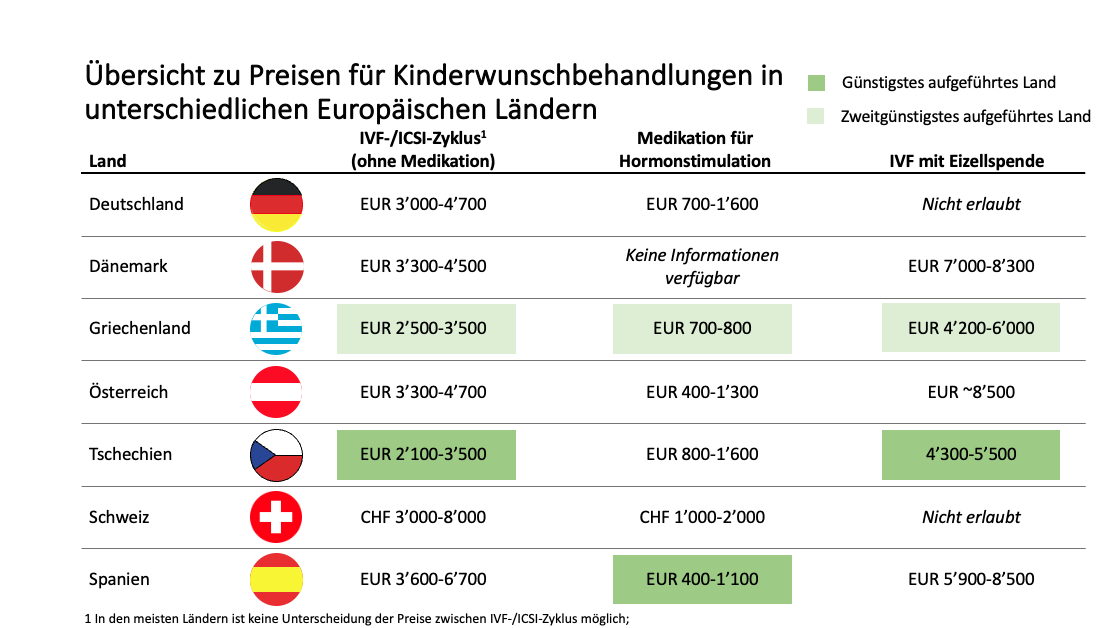
Sources: Fertilityroad.com; various fertility center price lists.
Here are a few more observations from the detailed country comparison:
A: Affluent countries in northern Europe generally have higher treatment costs than countries in southern and eastern Europe
B. Czech Republic and Greece are the most favorable countries in this comparison, the cost advantage becomes even greater here if egg donation is desired.
C: Spain is popular despite slightly higher costs than in the Czech Republic and Greece due to its good egg donor program and wide range of fertility clinics. Denmark is popular despite high treatment costs due to world’s leading sperm donor program
D: There are marked differences in the costs of hormone stimulation in different countries – moreover, these are almost always excluded in IVF / ICSI treatment packages and are only relatively rarely visible in price lists
2 Regulatory framework
In addition to cost, different treatments are allowed for different groups of people (by relationship status and sexuality) depending on the country. This can be a deciding factor in the choice of the country where the treatment is carried out. If, for example, due to the advanced age of the woman, only egg donation can be considered for successful IVF / ICSI treatment, the group of countries that can be considered for the patient shrinks.
In the following, we will first give an overview of the permitted treatment methods per country – in particular, egg donation is not permitted in all countries. Then we compare in which countries single women and lesbian couples can also undergo IVF / ICSI treatment.
2a: Treatment methods
Switzerland
Overall, Switzerland (similar to Germany and Austria) is relatively conservative with regard to approved treatment methods.
Permitted in Switzerland are:
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) with a transfer of maximum 3 embryos.
- Freezing of unfertilized and fertilized oocytes as well as embryos for a maximum of 2×5 years = 10 years
- Embryo development by day 5 (blastocyst culture) with resulting increased success rates per IVF transfer.
- Sperm donation – since 01 July 2022 also for female married couples – but conceived children have the right to know the identity of the sperm donor from the age of 18 and each donor is allowed to facilitate a maximum of 8 pregnancies
Prohibited in Switzerland are:
- Egg donation – in March 2022, however, the National Council approved a corresponding motion to legalize egg donation, and in September 2022 the Council of States also approved it. This mandates the Federal Council to create a legal basis for egg donation
- Embryo donation
- Surrogacy
- Preimplantation diagnostics (genetic testing of embryos conceived in a test tube) – exception: testing of the embryos’ chances of development in infertile couples and testing for hereditary diseases in couples with hereditary diseases.
Germany and Austria
For Swiss with an unfulfilled desire to have children, the neighboring countries of Germany and Austria naturally come into consideration for treatment; the cost of treatment here is lower than in Switzerland, but the regulatory situation is relatively similar to that in Switzerland:
| Germany | Austria | |
|---|---|---|
| Allowed are | – Intrauterine insemination (IUI) for all women – IVF / ICSI for all women – Sperm donation (children can request information about their father from the age of 16). |
– Intrauterine insemination (IUI) for heterosexual and lesbian couples – IVF / ICSI for heterosexual and lesbian couples – Sperm donation (children can request information about their father from the age of 14). – Egg donation (children can request information about their genetic mother from the age of 14). |
| Prohibited are | – Egg donation in general – Surrogacy |
– IUI / IVF / ICSI for single women – Surrogacy |
Other European countries
Here we give you a brief overview of the regulatory situation regarding treatment methods in Switzerland, Germany and Austria, as well as in the countries of Denmark, Greece, the Czech Republic and Spain, which are popular destinations for medical tourism for infertility treatments:

Sources: Fertility Europe – European Atlas of Fertility Treatment Policies (2021), VittoriaVita.
Main differences between countries:
- IVFI / ICSI treatments, as well as sperm donation are allowed in all countries
- Egg donation is allowed in all countries except Switzerland and Germany
- Surrogacy is allowed only in Greece, in Denmark and Czech Republic surrogacy is allowed only in non-commercial context
In almost all European countries, pre-implantation diagnostics is also permitted according to similar standards as in Switzerland, i.e. primarily for testing for hereditary diseases.
2b: Treatment of singles and homosexual couples
The following table provides an overview of access to IVF / ICSI treatments for heterosexual couples, lesbian couples and single women for Switzerland, Germany and Austria, as well as the currently most popular destinations for infertility treatment in Europe:

Sources: Fertility Europe – European Atlas of Fertility Treatment Policies (2021).
Here are a number of observations:
A: Together with Austria and the Czech Republic, Switzerland is one of the few countries in Europe that does not allow fertility treatment for single women.
B: Czech Republic is currently the most restrictive country in the comparison and does not allow fertility treatment for lesbian couples
C: Greece does not officially allow infertility treatment for lesbian couples, but this restriction can be circumvented by having one of the women treated as a single woman.
D: The other countries considered, Germany, Denmark, and Spain, all allow infertility treatment for all women regardless of sexual orientation or relationship status
3. conclusion
When choosing a place for treatment, in addition to the quality of the selected clinic, the expected cost of treatment and legal access to different treatment methods should be considered.
Although Switzerland is known for its excellent health care, access to fertility treatment is among the most expensive and restrictive in Europe. For example, patients can expect total costs of CHF 4,000 to CHF 9,000 for an IVF cycle and CHF 6,000 to CHF 10,000 for an ICSI cycle . Furthermore, there is currently no access to egg donation in Switzerland and fertility treatments are only available for heterosexual couples.
For Swiss and other Europeans with an unfulfilled desire to have children, a number of attractive countries with lower cost levels and relatively liberal regulatory regimes are available:
- Greece is among the two most favorable countries in the comparison listed here with IVF / ICSI treatment costs totaling EUR 3,200 to EUR 4,300. In addition, Greece is relatively liberal and allows access to egg donation and surrogacy, as well as fertility treatments for single women. For lesbian couples there is no official provision for infertility treatment, but one of the parents can register for treatment as a single woman without any problems.
- The Czech Republic is the most favorable country in the comparison listed here, with IVF / ICSI treatment costs totaling EUR 2,900 to EUR 5,100, access to egg donation and, in a non-commercial setting, surrogacy. However, infertility treatment in the Czech Republic is not offered to lesbian or single women.
- Spain is the most popular destination in Europe for infertility treatment, however, the price level has now increased due to the high demand and IVF / ICSI treatment costs range from EUR 4,000 to EUR 7,800 in total. In addition, Spain allows the use of egg donation and permits access to fertility treatment for all women regardless of sexual orientation or relationship status. Only the option of surrogacy is not available in Spain
Last update: November 28, 2022
Schwierigkeiten schwanger zu werden, aber die Kosten und Mühen einer Kinderwunsch-Behandlung schrecken Sie ab?
Griechenland gehört zu den europäischen Ländern mit den günstigsten Kinderwunsch-Behandlungen. Bei Kalimedica bringen wir Sie mit Kinderwunsch-Experten zusammen und unterstützen Sie auf Ihrer Reise zur Schwangerschaft



